• Autopoiesis, (self-referential)
Donna Haraway has introduced Sympoiesis to address precisely the problem of full autonomy.
She writes: Sympoieses means "making-with" Nothing makes itself.
Beyond our questions
regarding Autopoiesis, it was quite
surprising to read that the latter term is already regarded problematic:
“There are multiple criticisms of the use of the
term in both its original context, as an attempt to define and explain the
living, and its various expanded usages, such as applying it to self-organizing
systems in general or social systems in particular.[16] Critics
have argued that the term fails to define or explain living systems and that,
because of the extreme language of self-referentiality it uses without any external
reference, it is really an attempt to give substantiation to Maturana's radical constructivist or solipsistic epistemology.Donna Haraway has introduced Sympoiesis to address precisely the problem of full autonomy.
She writes: Sympoieses means "making-with" Nothing makes itself.
• Emergence
• EROEI
• Daoist (Taoist) Philisiophy
• Derridaoism
• Derrida Key Terms
• Desinterrance
• Gnosticim
• Immanence / Plane of Immanence
• Iterability
• Neo-Cybernetics
• EROEI
• Daoist (Taoist) Philisiophy
• Derridaoism
• Derrida Key Terms
• Desinterrance
• Gnosticim
• Immanence / Plane of Immanence
• Iterability
• Neo-Cybernetics
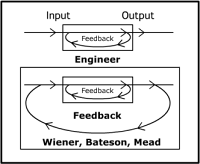
Neocybernetics is the term
adapted for this particular movement. In response to the apparent dissolution
of boundaries at work in the contemporary technosciences of emergence,
neocybernetics observes that cognitive systems are operationally bounded,
semi-autonomous entities coupled with their environments and other systems. Second-order systems theory stresses
the recursive complexities of
observation, mediation, and communication. Focused on neocybernetics, the most
prominent players are Foerster,Chilenial biologists Francisco Varela and Humberto Maturana and Niklas Luhmann, the
latter especially with his adaptations of autopoiesis to social systems
theory. (source: Emergence and
Embodiment)
• Neo-Darwinism
• Recursion
• Re-mark
• Second-order systems theory
Cybernetics and Systems Theory
In
1940s, the first cybernetics—the study of communication and control systems—was
mainstreamed under the names artificial intelligence and computer science and
taken up by the social sciences, the humanities, and the creative arts. The
systems theory Emergence focuses on cybernetic developments
that stem from the second-order turn in
the 1970s, when the cyberneticist Heinz von Foerster catalyzed new thinking
about the cognitive implications of self-referential
systems. The crucial shift he inspired was from first-order cybernetics’
attention to homeostasis as a mode of autonomous self-regulation in mechanical
and informatic systems, to second-order concepts of self-organization and
autopoiesis in embodied and metabiotic systems.
First-order and Second-order is not
exclusively links to Systems theory. Second-order generally indicates an
extended or higher complexity. The way I recalled it was in relation to
emergent structures, which I was not able to real that here the second order is
actually the temporal dimension, it’s a beautiful poetic detail in evolutionary
geology:
“It is useful to distinguish
three forms of emergent structures. A first-order emergent structure occurs as a result of shape interactions
(for example, hydrogen bonds in water molecules lead to surface tension). A second-order emergent structure involves shape interactions played out
sequentially over time (for example, changing atmospheric conditions as a
snowflake falls to the ground build upon and alter its form). Finally, a third-order emergent structure is a consequence of shape,
time, and heritable instructions. For example, an organism's genetic code sets
boundary conditions on the interaction of biological systems in space and
time.”
• Social Darwinism
• Social Darwinism
• ( solipsistic) Neo-Kantian Idelialism